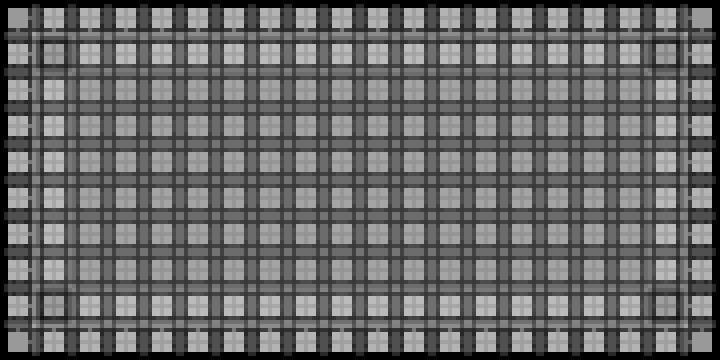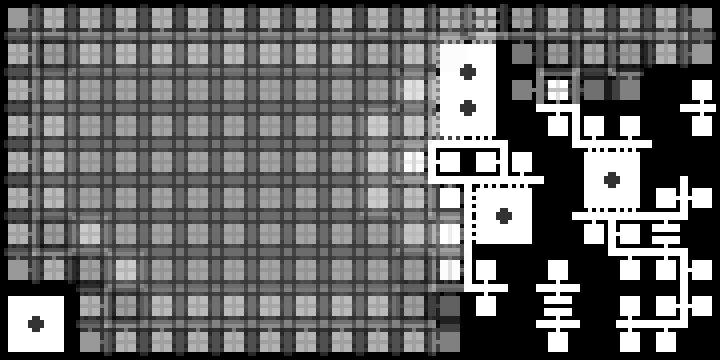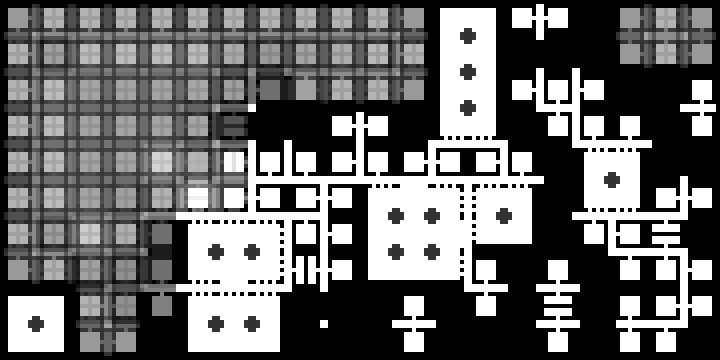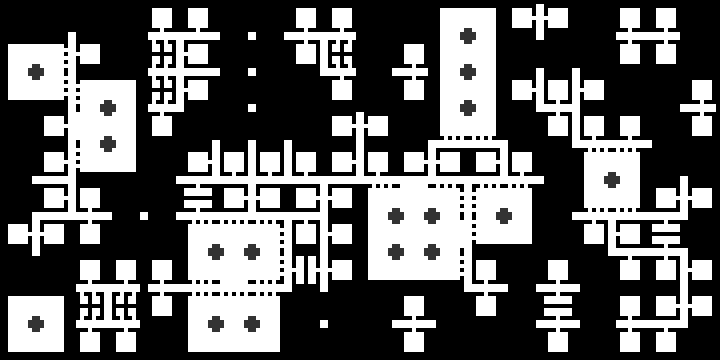
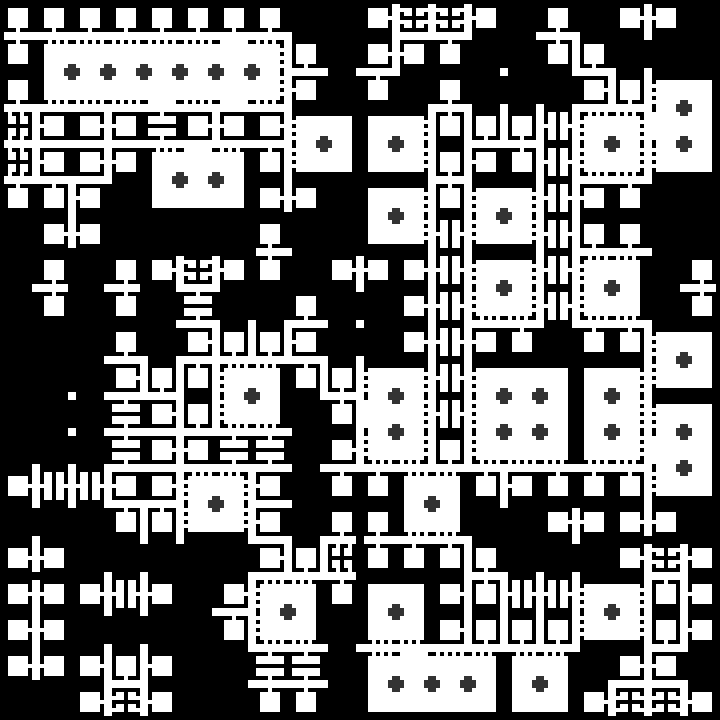
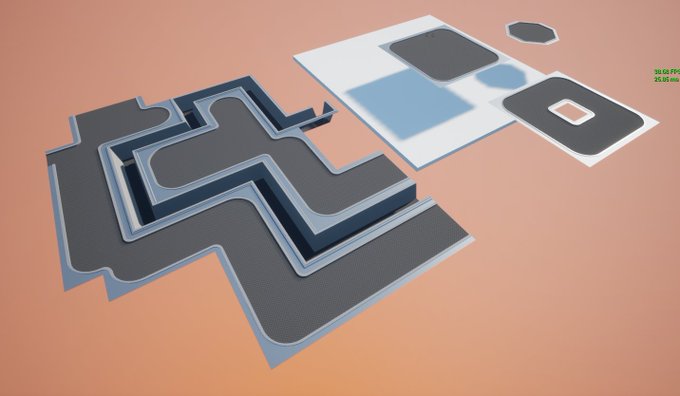
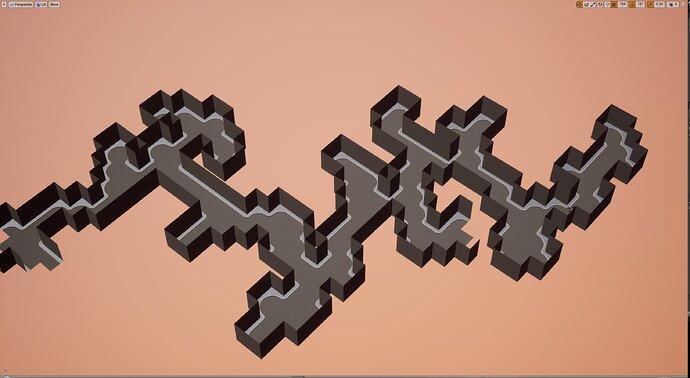
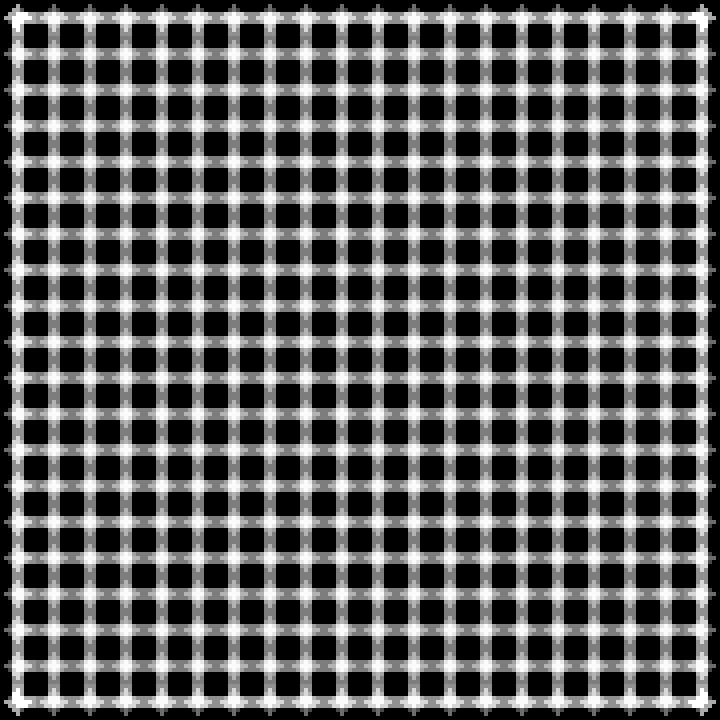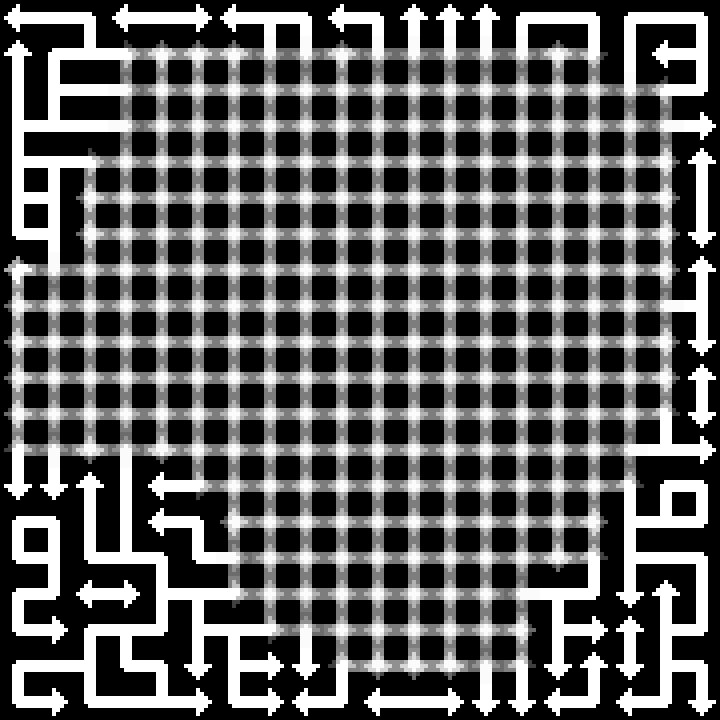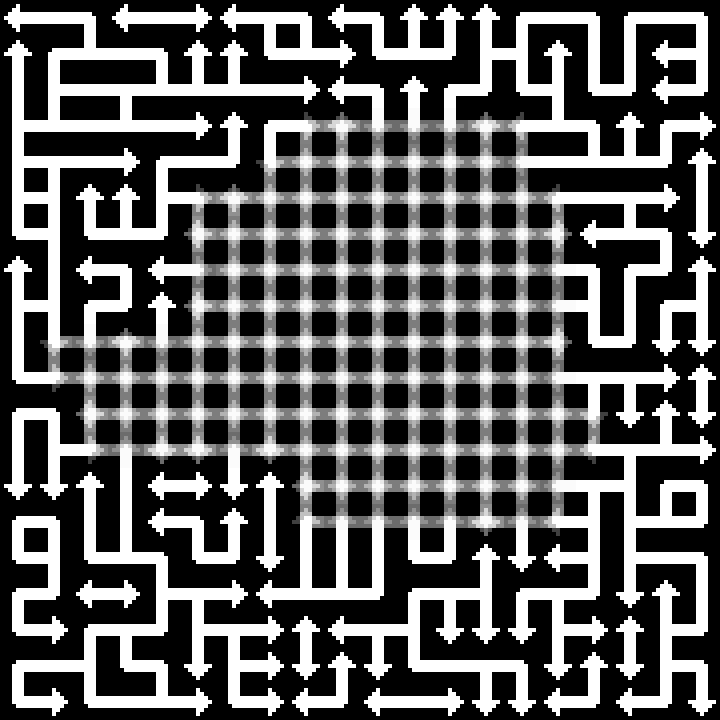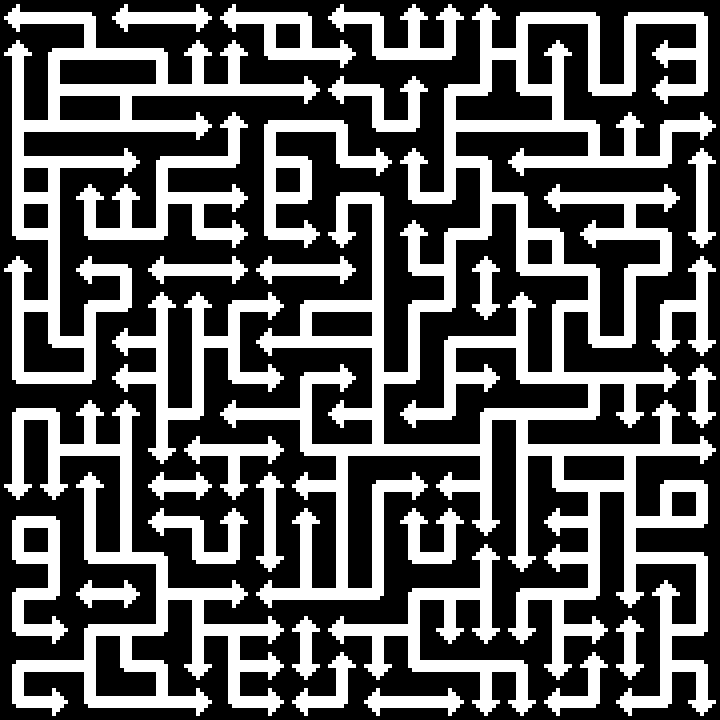
I should post my (very scrappy and slow) code too. It does not seem to work with latest version of numpy, but installing numpy 1.23.4 helped.
Gif generation must be enabled in the script, but it makes it waaay slower.
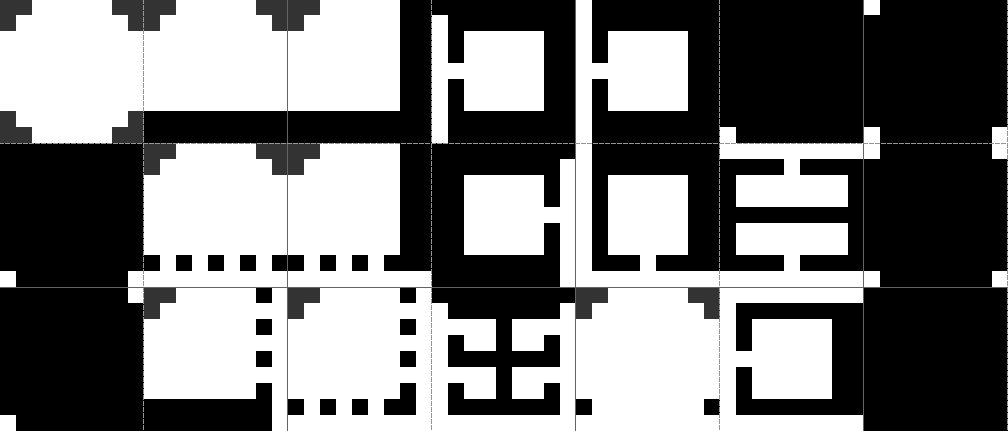
These are the tilesets

from PIL import Image
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import List
import random
import calendar
import time
import numpy
from blend_modes import addition
@dataclass
class Tile:
content: Image
edge_n: tuple[int,int,int,int,int,int,int,int,int]
edge_s: tuple[int,int,int,int,int,int,int,int,int]
edge_w: tuple[int,int,int,int,int,int,int,int,int]
edge_e: tuple[int,int,int,int,int,int,int,int,int]
name: str
@dataclass
class Neighbor:
x: float
y: float
edge_name: str
TILE_SIZE = 9
tile_types = []
im = Image.open("tileset.png")
tileset_w = im.size[0] // TILE_SIZE
tileset_h = im.size[1] // TILE_SIZE
def rgba_to_int( rgba ):
return rgba[0]
for x in range(tileset_w):
for y in range(tileset_h):
tile_data = im.crop((x*TILE_SIZE, y*TILE_SIZE, (x+1)*TILE_SIZE, (y+1)*TILE_SIZE))
#ix = list(tile_data.getdata())
#edge_n = map(rgba_to_bool, pix[:,0])
edge_n = tuple(map(rgba_to_int, list(tile_data.crop((0,0,TILE_SIZE,1)).getdata())))
edge_s = tuple(map(rgba_to_int, list(tile_data.crop((0,TILE_SIZE-1,TILE_SIZE,TILE_SIZE)).getdata())))
edge_w = tuple(map(rgba_to_int, list(tile_data.crop((0,0,1,TILE_SIZE)).getdata())))
edge_e = tuple(map(rgba_to_int, list(tile_data.crop((TILE_SIZE-1,0,TILE_SIZE,TILE_SIZE)).getdata())))
tile_types.append( Tile(tile_data, edge_n, edge_s, edge_w, edge_e, str(x)+"_"+str(y)+"_0") )
if edge_n == edge_s and edge_w == edge_e:
if edge_n != edge_w:
tile_types.append( Tile(tile_data.rotate(90), edge_e, edge_w, tuple(reversed(edge_n)), tuple(reversed(edge_s)), str(x)+"_"+str(y)+"_90") )
else:
tile_types.append( Tile(tile_data.rotate(90), edge_e, edge_w, tuple(reversed(edge_n)), tuple(reversed(edge_s)), str(x)+"_"+str(y)+"_90") )
tile_types.append( Tile(tile_data.rotate(180), tuple(reversed(edge_s)), tuple(reversed(edge_n)), tuple(reversed(edge_e)), tuple(reversed(edge_w)), str(x)+"_"+str(y)+"_180") )
tile_types.append( Tile(tile_data.rotate(270), tuple(reversed(edge_w)), tuple(reversed(edge_e)), edge_s, edge_n, str(x)+"_"+str(y)+"_270") )
field_w = 20
field_h = 20
wfc_field = [[0 for y in range(field_h)] for x in range(field_w)]
edge_names = ["edge_n", "edge_w", "edge_s", "edge_e"]
for field_x in range(field_w):
for field_y in range(field_h):
possibilities = []
for tile in tile_types:
possibilities.append(tile)
wfc_field[field_x][field_y] = possibilities
def remove_edge_possibility(x, y, edge_name, edge_def):
possibilities = wfc_field[x][y].copy()
for tile in possibilities:
if getattr(tile, edge_name) == edge_def:
remove_possibility(x, y, tile)
def set_only_edge_possibility(x, y, edge_name, edge_def):
possibilities = wfc_field[x][y].copy()
for tile in possibilities:
if getattr(tile, edge_name) != edge_def:
remove_possibility(x, y, tile)
def remove_possibility(x, y, tile_type):
if tile_type not in wfc_field[x][y]:
return
wfc_field[x][y].remove(tile_type)
edge_type_use_counts = [0, 0, 0, 0]
for tile in wfc_field[x][y]:
for i, edge_name in enumerate(edge_names):
if getattr(tile_type, edge_name) == getattr(tile, edge_name):
edge_type_use_counts[i] += 1
for i, _ in enumerate(edge_type_use_counts):
if edge_type_use_counts[i] == 0:
neighbor = get_neighbor(x, y, edge_names[i])
if neighbor is not None:
neighbor_edge_def = getattr(tile_type, edge_names[i])
remove_edge_possibility(neighbor.x, neighbor.y, neighbor.edge_name, neighbor_edge_def)
edge_type_use_counts = [0, 0, 0, 0]
for tile in wfc_field[x][y]:
for i, edge_name in enumerate(edge_names):
if getattr(tile_type, edge_name) == getattr(tile, edge_name):
edge_type_use_counts[i] += 1
def collapse_to_possibility(x, y, tile_type):
if tile_type not in wfc_field[x][y]:
return
possibilities = wfc_field[x][y].copy()
for tile in possibilities:
if tile != tile_type:
remove_possibility(x, y, tile)
def collapse_to_random_possibility(x, y):
tile_type = random.choice(wfc_field[x][y])
collapse_to_possibility(x, y, tile_type)
#print("tile "+str(x)+" "+str(y)+" collapsed. Possibilities: " + str(len(wfc_field[x][y])))
if (len(wfc_field[x][y]) > 1) :
print(list(map(lambda a : a.name, wfc_field[x][y])))
def get_neighbor(x, y, edge_name):
if edge_name == "edge_n":
y -= 1
neighbor_edge_name = "edge_s"
if edge_name == "edge_s":
y += 1
neighbor_edge_name = "edge_n"
if edge_name == "edge_w":
x -= 1
neighbor_edge_name = "edge_e"
if edge_name == "edge_e":
x += 1
neighbor_edge_name = "edge_w"
if x < 0 or x >= field_w or y < 0 or y >= field_h:
return None
return Neighbor(x, y, neighbor_edge_name)
edge_empty = (0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0)
for x in range(field_w):
set_only_edge_possibility(x, 0, "edge_n", edge_empty)
set_only_edge_possibility(x, field_h-1, "edge_s", edge_empty)
for y in range(field_h):
set_only_edge_possibility(0, y, "edge_w", edge_empty)
set_only_edge_possibility(field_w-1, y, "edge_e", edge_empty)
def find_least_uncertainty():
least_uncertainty = len(tile_types)
candidates = []
for x in range(field_w):
for y in range(field_h):
if (len(wfc_field[x][y]) <= 1):
continue
if (len(wfc_field[x][y]) < least_uncertainty):
least_uncertainty = len(wfc_field[x][y])
candidates = [(x,y)]
elif (len(wfc_field[x][y]) == least_uncertainty):
candidates.append((x,y))
if len(candidates) == 0:
return False
x, y = random.choice(candidates)
collapse_to_random_possibility(x, y)
return True
def make_image():
dungeon_map = Image.new('RGB', (field_w*TILE_SIZE, field_h*TILE_SIZE), (0,0,0))
for x in range(field_w):
for y in range(field_h):
if len(wfc_field[x][y]) > 0:
offset = (x * TILE_SIZE, y * TILE_SIZE)
blend = Image.new('RGBA', (TILE_SIZE, TILE_SIZE), (0,0,0))
blend_np = numpy.array(blend).astype(float)
#tile = random.choice(wfc_field[x][y])
for tile in wfc_field[x][y]:
im = tile.content.point(lambda a: a*(1.0/len(wfc_field[x][y])))
im.putalpha(255)
im_np = numpy.array(im).astype(float)
blend_np = addition(blend_np, im_np, 1.0)
blend = Image.fromarray(numpy.uint8(blend_np))
dungeon_map.paste(blend, offset)
dungeon_map = dungeon_map.resize((field_w*TILE_SIZE*4, field_h*TILE_SIZE*4), Image.NEAREST)
return dungeon_map
frames = []
duration = []
make_gif = False
if make_gif:
frames.append(make_image())
duration.append(100)
snapshot_step = 1
iter_counter = snapshot_step
while find_least_uncertainty():
iter_counter -= 1
if iter_counter == 0:
if make_gif:
frames.append(make_image())
duration.append(100)
iter_counter = snapshot_step
# collapse_to_random_possibility(1, 1)
# collapse_to_random_possibility(2, 2)
# collapse_to_random_possibility(3, 3)
# collapse_to_random_possibility(4, 4)
# collapse_to_random_possibility(5, 5)
if make_gif:
frames.append(make_image())
duration.append(1000)
for x in range(field_w):
print(list(map(len, wfc_field[x])))
if make_gif:
frames[0].save("map_generation_"+str(calendar.timegm(time.gmtime()))+".gif", save_all=True, append_images=frames[1:], duration=duration, loop=0)
dungeon_map = make_image()
dungeon_map.show()
dungeon_map.save("map"+str(calendar.timegm(time.gmtime()))+".png")